What is an Ohmmeter?
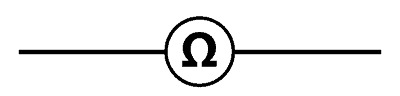
An ohmmeter is an electrical instrument used to measure the resistance in a circuit or a component. The opposition to the flow of electric current is a measure of resistance in the electrical circuit. The unit of electrical resistance is ohms (Ω).
Ohmmeter works based on when an ohmmeter applies current to the circuit or component, it measures the resulting voltage and calculates the resistance value using ohms law formula V=IR. To measure resistance, we can also use an analog multimeter and digital multimeter.
We cannot find out the resistance using ohmmeter in a working or test circuit. To check the resistance, we need to disconnect the power and measure the resistance.
Construction
The construction of the ohmmeter circuit is a mix of milliammeter (microammeter) with a set of resistances in series and a constant battery source. The analog multimeter consists of following parts:
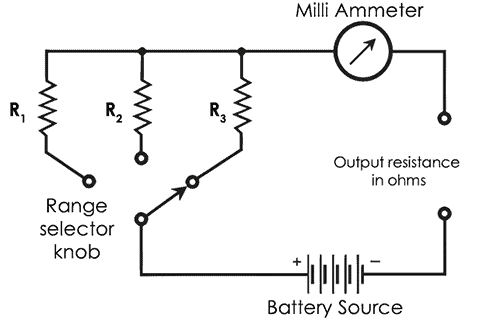
- Display: Different scales are shown for measuring different electrical quantities. Non-linear ohmmeter scale is present on the top of it.
- Pointer: It indicates the value of measurement on the scale. It deflects or moves based on resistance value.
- Range selector knob: There is a knob at the center to select different functions
- MilliAmmeter or Microammeter: For a given constant voltage, the current through the ammeter will change if the resistance changes. This will give the output resistance in ohms (Ω).
- Multimeter Dial: The rotary dial surrounds the knob which has the different range selectors
- Jack/Ports: There are two input jacks to connect the probes
- Probes/Leads: It comes with two probes- Black probe and the red probe
How does an Ohmmeter Work?
The working principle of Ohmmeter is, when current flow through the circuit or component, the pointer deflects in the meter. When a pointer moves the left side of the meter, it represents a high resistance and responds to low current.
When the pointer deflects to the right side of the meter, it represents a low resistance and responds to high current. You can look at the scale on the below image:
The resistive measuring scale is nonlinear in an ohmmeter and the analog multimeter. The resistance measuring meters pointer is reading zero at the full scale (right side) and maximum at the rest. We need to make a pointer position to zero before using it.

After it comes down to zero, we can test the component. The resistance meter usually will range from 1 ohm(1Ω) to 1megaohm (1MΩ). When the two probes are connected at each side of the resistor, the pointer starts to deflect.
To know, how to read an ohmmeter, Turn the selector knob to an estimated ohms range or set it to the maximum range to see if you are getting the estimated reading. If the value is too high, the pointer will stay on zero. We can try adjusting the dial of resistance range to one lower multiplier range or keep adjusting the knob until we obtain accurate results.
After the completion of knob adjustments, we need to make the calculations with the results we read on the scale. If the multiplier range is marked as ‘x10’, we need to multiply the reading by 10 ohms. If the multiplier range marking is written as ‘x1K’, we need to multiply the reading by 1000 ohms.
Types of Ohmmeter
There are different types of ohmmeter based on construction. They are Micro, Milli, Mega, digital multimeter, series, shunt, and Multirange ohmmeter.
-
Micro-Ohmmeter
This ohmmeter measures relatively low resistance in the range of 1µΩ to 2500Ω. The meter consists of a set of resistances with different current ranges.
It uses a 4-wire Kelvin method for measuring the resistance of inductive loads. It uses Filters to eliminate AC ripples. Some of them are 10A-5mΩ, 10A-25mΩ, 10A-250mΩ, 1A-2500mΩ, 100mA-25Ω, 10mA-250Ω, 1mA-2500Ω.
-
Milli-Ohmmeter
The digital milli-ohmmeter calculates resistance in the range of 100 µΩ to 2000Ω with high accuracy. It uses a 4-wire resistance technique for measuring resistance.
The applications are winding resistance measurement for electric motors, generators, Bond testing for railways, ships, etc.
-
Mega ohmmeter (Megger)
Megger instrument measures Megaohms and Giga-ohms resistance in a circuit. It is suitable for insulation resistance measurement. The measuring range of the meter is 0.5Ω to 2, 000, 000 MΩ.
-
Digital Ohmmeter
This is also known as a digital multimeter for resistance measurement. It also measures current and voltage in an electronic circuit. This meter is easy to read when compared with the analog one. You can measure the resistance in ohms, kilo-ohms, and mega ohms in a digital display.
-
Series Ohmmeter
This instrument measures high resistance values for the device under test (DUT). For this, it uses two resistors (series and zero adjust) to find out unknown resistance across the resistor.
The zero adjust resistor is in parallel with D’ Arsonval (meter movement). The device has an internal source voltage to produce current and shows resistance through meter deflection.
-
Shunt Ohmmeter
Shunt meter measures low resistance values in a circuit. The infinity reading is adjusted instead of zero resistor. This type of ohmmeters is not used as their measuring range is low (5 to 400 Ω).
Unlike series type, this meter movement is in parallel with the resistance to be found.
-
Multirange Ohmmeter
To measure a wide range of resistance values, this meter provides a selection switch. The initial reading is set to zero using adjuster. To know unknown resistance, connect it in parallel to the instrument. The adjustment is done such that, the meter shows full-scale value.
Comparison
Here are some of the applications and uses of an ohmmeter.
| Ohmmeter Type | Uses |
|---|---|
| Micro | Measures resistance for motors, transformers, components, circuit breakers and switches, RTD measurements |
| Milli | Voltage and current measurement, Testing diodes, PCB tracks, etc. |
| Mega | Insulation cables, Testing of capacitors, Grounding, and short circuit testing |
| Digital | Measures voltage, resistance (Ω, kΩ, MΩ) and currents |
| Series- type | High resistance measurements, machine field coils |
| Shunt type ohmmeter | Find outs low resistance values, Precision bridge circuit, heater elements |
Conclusion
Finally, how to measure the resistance using Ohmmeter and which type? It depends on the measuring circuit and application. The ohmmeter measures the resistance between the two leads.
Here is an interesting question for you. When an open resistor, when checked with an ohmmeter, reads how many ohms?
The answer is, if you short the leads, there is no resistance in the circuit and meter will display zero ohms. When the probes are not connected, the circuit is open and the meter will show infinite resistance.