Electronics is an applied form of science that deals with electrons. It handles electric circuits containing active elements, passive elements and other underlying techniques making it as an important part of engineering. The world is growing at a fast rate and it is relevant for the technology enthusiast to upgrade with latest changes happening in the society. Moreover, it is difficult to spend few hours without electronics gadgets and they had become an important part of our everyday routine.
Need of Electronics
We are living in an electronic era where machine robots are capable to do human work with more ease and high efficiency. Capsules and tablets contain wireless sensors that collect information from the body to diagnose. Transparent smartphones will exist in the coming days, we can see through them and they may lead to the use of windows or mirrors in our home to be used as PC screens and TV monitors. Sensors are placed on the plants to detect the shortage of water and alert the farmers.
Not only above applications, there are numerous electronic applications that change our daily lives in the nearby future.
Electronic devices are made up of active and passive elements and smaller IC memories. The ICs, diodes, and transistor are made of semiconductor materials and their working is dependent on current flow through them.
History of Electronics
- Vacuum Diode – Invented by John Ambrose Fleming
Electronics era came into existence with the invention of vacuum diode in the year 1897. Vacuum tube essentially consists two electrode plates i.e. anode and cathode. This allows current direction in one direction. But this diode is not able to control the current flow. In 1906 Lee De Forest modified and named it as Vacuum Triode. The Triode has 3 terminals. Anode, Cathode and Grid terminal. Grid electrode controls the current flow from anode to cathode. This feature could boost the power of electrical signals. Likewise, Tetrode and Pentode had evolved.
- Transistor – Invented by John Bardeen, Walter Brattain and William Shockley
The real development started with the invention of the transistor in 1948 in Bell Laboratories. Large Bulky Vacuum diodes are replaced with junction transistor.
Transistors are initially made with germanium material, later on, silicon BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) are grown up. Most of the devices developed today are made up of silicon only due to its low cost.
- IC (Integrated Circuit) – Jack Kilby
To reduce the size and cost of the entire circuit Jack Kilby introduced a new concept. This idea entirely changed the world. The complete interconnected circuit is placed on a single chip commonly called VLSI (Very Large Scale Integrated). Computer processors used today are made up of billions of transistors integrated on a single IC.
What is Electronics?
“Electronics”, as the name implies relating to electrons. The word electronics arrived from electron mechanics (Behaviour of the electron when it is subjected to externally applied fields).
The definition of electronics technically says “Electronics is an engineering branch that concerns with the flow of current through semiconductor, gas or any form of matter.
Applications of Electronics
-
Consumer Electronics

This industry is most applicable to the common people. Consumer Electronics are devices and equipment meant for everyday use. This is again categorized as:
Office Gadgets such as calculators, Personal computers, Scanners and Printers, FAX machine, Front Projector etc.
Home appliances such as Washing Machine, Refrigerator, Air Conditioner, Microwave Oven, Vacuum Cleaner etc.
Audio and Video Systems such as Headphone, VCRs, DVD players, Color TVs, Microphone and Loudspeaker, Video game consoles.
Advanced Consumer Devices such as Setup Box, ATM, Dishwasher, Smart Phones, PDA (personal digital assistant), Barcode Scanners, POS terminals.
Storage Devices for optical playback and taping, and portable infotainment. Examples are DVDs, HDD jukebox, Portable MP3 player.
-
Industrial Electronics

This industry is powerful in making real-time automation. This include:
Industrial automation and motion control, Machine learning, motor drive control, Mechatronics and robotics, Power converting technologies, Photo voltaic systems, Renewable energy applications, Power electronics, and Biomechanics.
Smart grid systems
Smart electric systems collect information from the communication technology and react accordingly based on power consumption. It is an application of intelligence, computing, and networked electricity systems.
Example: Smart Meters
Features of smart grid
- Digital system based on two-way communication
- Interactive Sensors
- Self-monitoring and Debugging
- Valid Distribution of electricity
Industrial automation and motion control
Machines are replacing humans these days with increased productivity, time and cost. Moreover, safety is also considered for unmanageable works. Hence to delegate the human’s, automation has become the preferable choice for industries.
Image processing
3D world has been evolved from a single or multiple 2D images. Various algorithms are developed to extract 3D information from 2D patterns.
Moreover, image processing has involved in computer graphics, Artificial intelligence, Robotics for navigation, Inspection and Assembly, Computer Vision for Face and gesture recognition, Virtual reality, medical analysis.
-
Medical applications
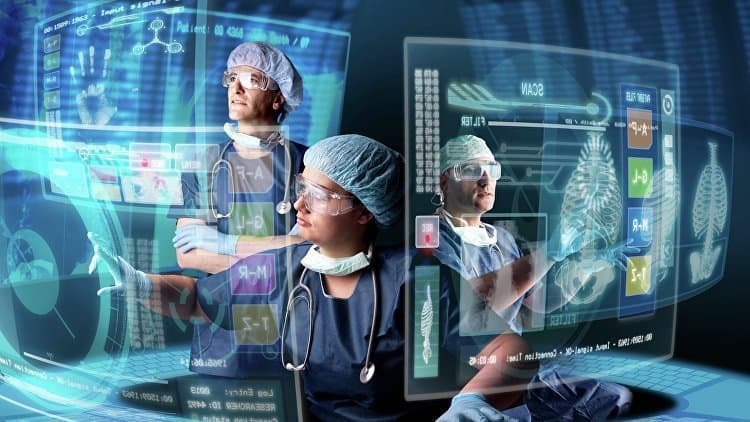

Advanced sophisticated instruments are being developed for data recording and physiological analysis. They are proven to be more useful in diagnosing diseases and for healing purpose.
Some of the medical devices and equipment used are:
- Stethoscope to listen inner sounds happening inside the human or animal body
- Respiration Monitors for knowing the patient condition due to change in body temperature, pulse, respiration and blood flow.
- Defibrillator causes electrical shock to heart muscles and brings backs the heart to the normal working condition.
- Glucose meter for measuring sugar levels in the blood.
- Pace Maker for reducing and increasing the count of the heart beat.
-
Meteorological and Oceanographic
Environmental monitoring is done through various sensors and Automatic weather stations. Some of them are:

- Barometer for predicting the weather is good or bad. It gives atmospheric pressure level as an indication. If pressure level is high weather is good and if pressure is low it means the weather is bad.
- Anemometer measures the wind speed and wind direction
- Tipping Bucket Rain gauge for measuring the rainfall periodically stored in the Automatic weather station such as Datalogger.
- Hygrometer measuring Humidity
- Drifter Buoy measures current, temperature, and pressure levels in the ocean
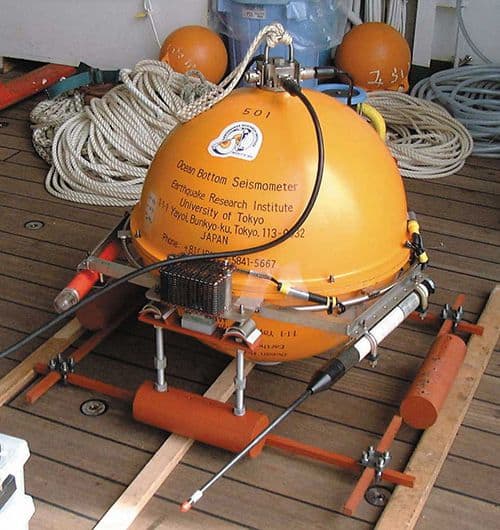

- Data logger for storing the data collected from various sensors like humidity, temperature, wind speed and direction, solar radiation, Rain scale.
-
Defence and Aerospace

Defence and Aeronautical applications include:
- Missile Launching systems
- Rocket Launchers for space
- Aircraft systems
- Cockpit controllers
- Military Radars
- Boom barrier for military applications
-
Automotive (Automobiles)
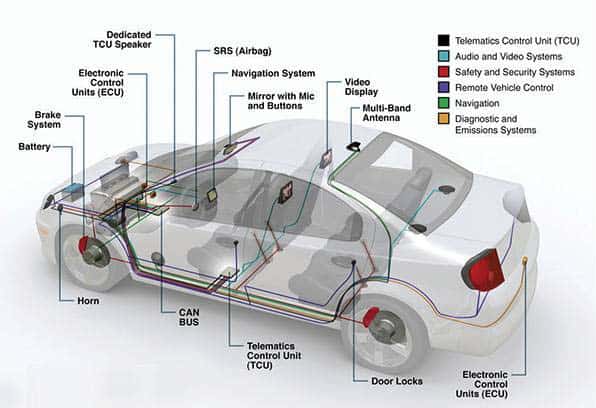
- Anti-collision unit
- Infotainment console
- Anti-lock braking system
- Cruise control
- Traction control
- Window regulators
- Electronic Control Unit (ECU)
- Airbag control
Conclusion
Electronics is having a great scope and without electronic gadgets, our daily lives cannot happen. Technology is advancing quickly in the field of semiconductors and upgraded electronic applications will shape the world.



Great article! Thumbs up!
Very nice and useful. Great
Thanks to yr contributions
Very interesting
What are the applications of EDC(Electronic devices and Circuits) in electrical engineering
It’s very useful tq so much…
Nice information… Thank you so much
This is much more updated information for interested students and teachers.
good performance technology I want to be one of them
great work . loved it. kudos
Great work very useful 🙏
Great work very useful,thanks